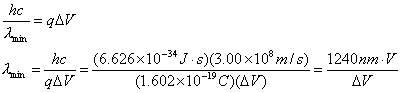![]() Physics
2056 Assignment # 4W Due:
Physics
2056 Assignment # 4W Due:
- Using the notation
described in your textbook (1s22s2, etc.) write down the electronic
configuration for (a) Ca and (b) As.
SOLUTION
(a) Ca: 1s22s22p63s23p64s2
(b) As: 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p3
- Write down the
possible sets of the four quantum numbers when the principal quantum
number n = 3.
SOLUTION
n l ml ms
3 0 0 +/-
½
3 1 1 +/-
½
3 1 0 +/-
½
3 1 -1 +/-
½
3 2 2 +/-
½
3 2 1 +/-
½
3 2 0 +/-
½
3 2 -1 +/-
½
3 2 -2 +/-
½
- List the possible
sets of quantum numbers for electrons in (a) the 3d subshell and (b) the 3p
subshell.
SOLUTION
(a) 3d: (n = 3, l =
2)
n l ml ms
3 2 2 +/-
½
3 2 1 +/-
½
3 2 0 +/-
½
3 2 -1 +/-
½
3 2 -2 +/-
½
(b)
3p: (n = 3, l = 1)
n l ml ms
3 1 1 +/-
½
3 1 0 +/-
½
3 1 -1 +/-
½
- Calculate the magnitude
of the orbital angular momentum for an electron in (a) the 4d state and (b) the 6f state.
SOLUTION
(a) 4d: ![]()
(b) 6f: ![]()
- The principal quantum
number for an electron in an atom is n
= 6, while the orbital magnetic quantum number is ml = 2. What
possible values for the orbital quantum number l could this electron have?
SOLUTION
![]()
- An electron in an
atom has a value for the orbital magnetic quantum number of ml = 4. What are the minimum values that (a) the
orbital quantum number and (b) the principal quantum number can have?
SOLUTION
(a) ![]()
(b) ![]()
- For an electron in a
hydrogen atom, the z component of the angular momentum has a maximum value
of Lz = 2.11 x 10-34
J·s. Find the three smallest
possible values (algebraically) for the total energy (in eV) that this
atom could have.
SOLUTION
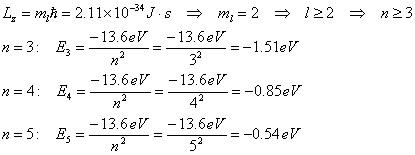
- For the hydrogen
atom, the Bohr model and quantum mechanics both give the same value for
the energy of the nth
state. However, they do not give
the same value for the orbital angular momentum L. (a) For n = 1, determine the values of L (in units of h/2π) predicted by the Bohr model and quantum
mechanics. (b) Repeat part (a) for n = 2, noting that quantum
mechanics permits more than one value of l when the electron is in the n = 2 state.
SOLUTION
(a) Bohr ![]() ;
;
Q. M. ![]()
(b) Bohr ![]() ;
;
Q. M. ![]() ;
; ![]()
- Suppose the
ionization energy of an atom is 4.10 eV.
In the spectrum of this same atom, we observe emission lines with
wavelengths 310 nm, 400 nm and 1378 nm.
Use this information to construct the energy-level diagram with the
fewest levels. Assume that the
higher levels are closer together.
SOLUTION
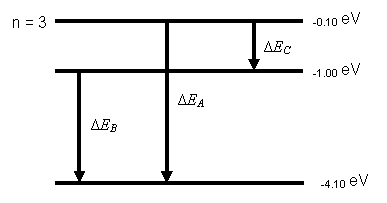
n = 2
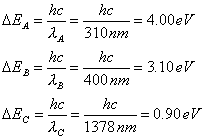
n = 1
- In x-ray production,
electrons are accelerated through a high voltage ΔV and then decelerated by striking a target. Show that the shortest-wavelength x-ray
that can be produced is
![]()
SOLUTION