Home
Research
Group Members and Recent Theses
Publications
Teaching
Outreach Activities
Research in the Department
Biophysics in Canada
|
DEMONSTRATION TOPICS
Low Temperature and
Thermal Physics
Mechanical and Energy
Sound
Electricity and
Magnetism
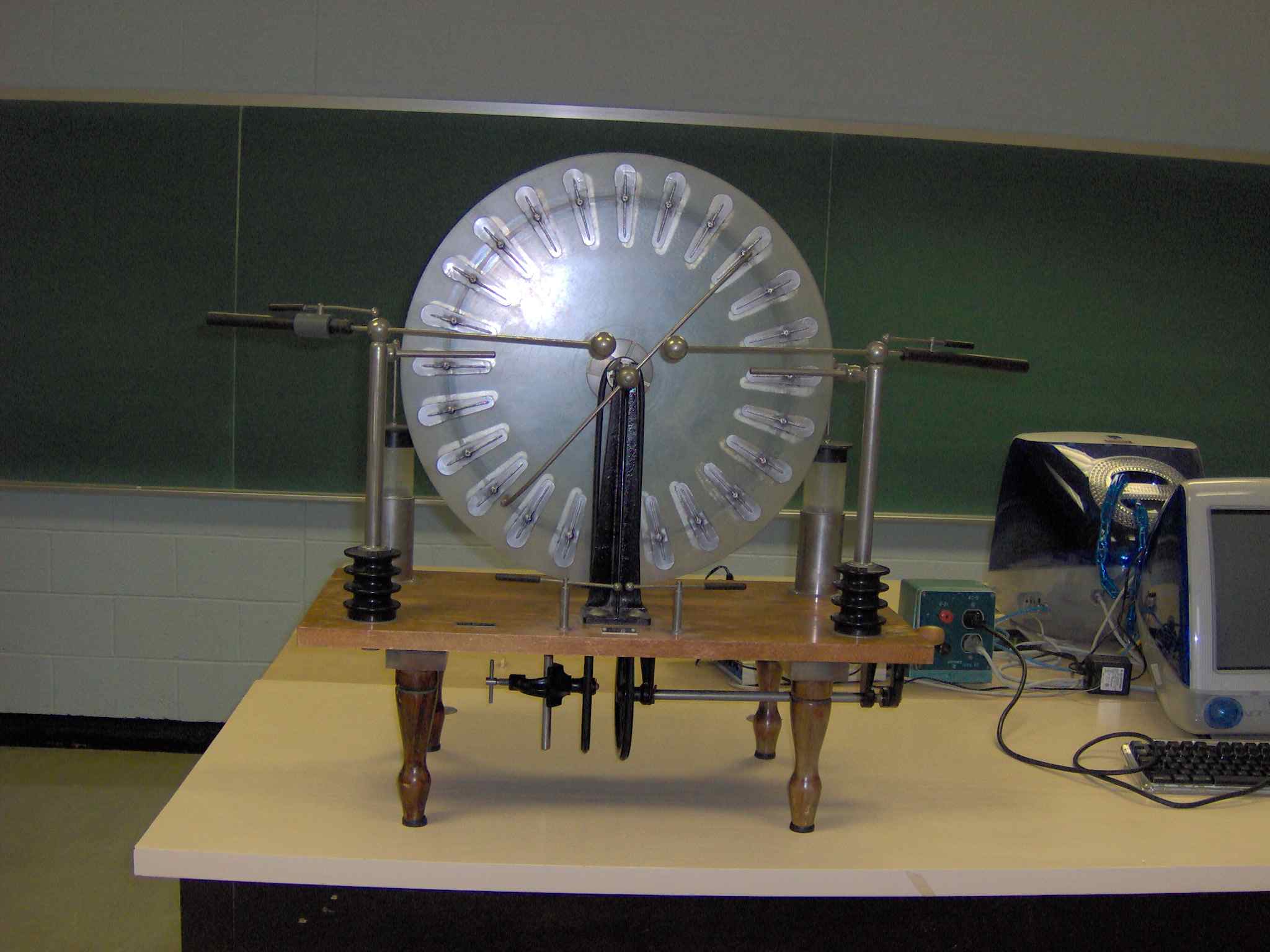
This is a Whimhurst electrostatic generator. When the crank is turned, two glass
disks rotate in opposite directions and aluminum pads on the discs are charged by electrostatic
induction. Charge is removed from the pads by needles just above the disc
surfaces. The charge is stored in Leyden jars until the electrostatic field between two
spheres is high enough to ionize air and a spark jumps between them.
| 
The Crooke's tube is an evacuated tube in which electrons can be accelerated by
a large potential difference. The phosphor screen glows when hit by electrons.
A magnetic field perpendicular to the electron path exerts a force perpendicular
to both. This can be used to demonstrate how magnetic fields can be used to
steer electrons beams in devices like a television screen or a cathode ray tube
(CRT).
|
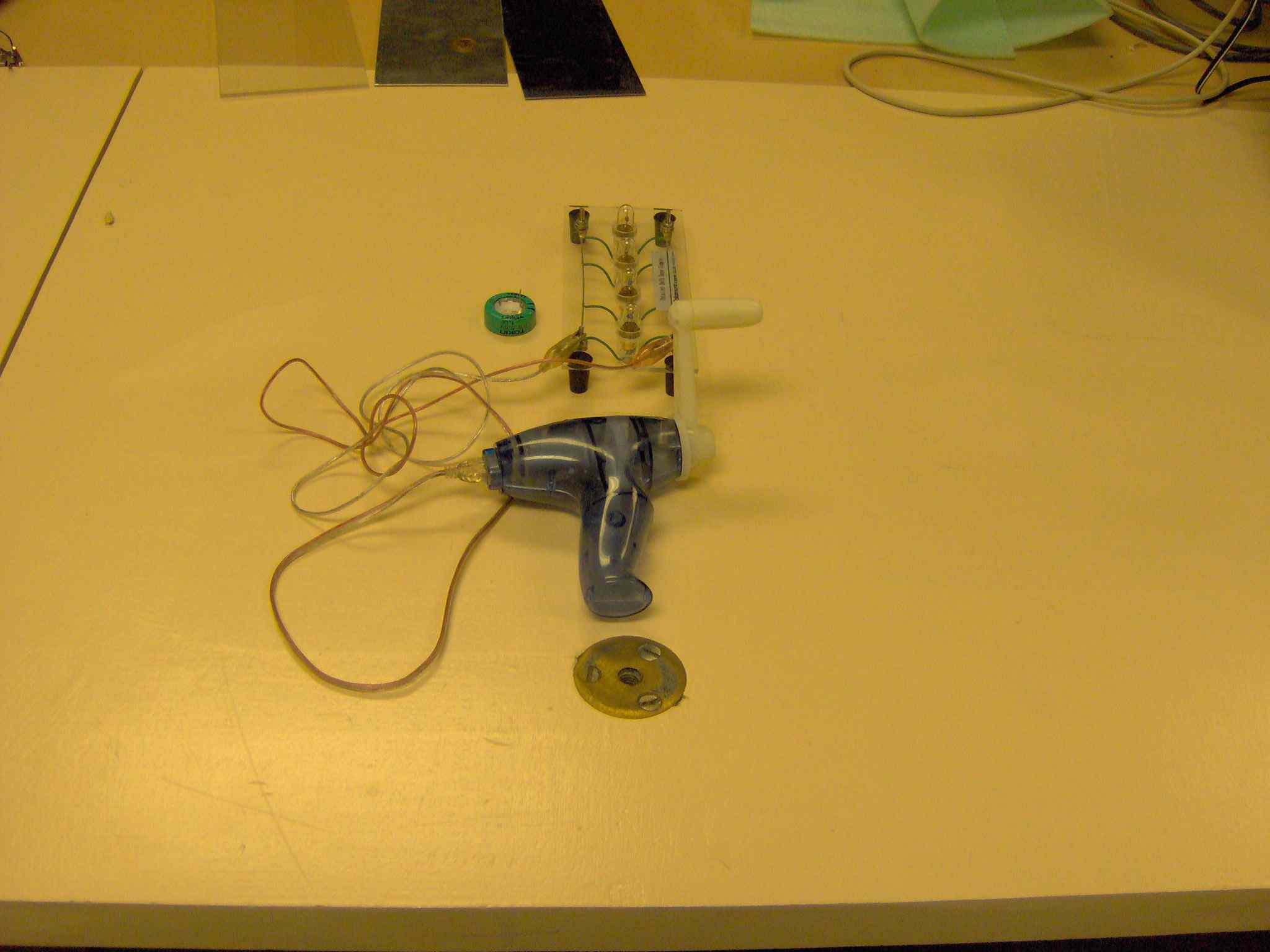
The force exerted on electrons as they cross magnetic field lines can be used to
generate current as in this generator. If the wires from the generator are not
connected to anything, the generator does no work and its handle turns easily.
If the generator is pushing electrons through resistance (like light bulb
filaments) the handle is harder to turn. The generator can push electrons into
a storage device like a capacitor. When you stop turning the handle, the
electrons flow back through the generator and it acts like an electric motor.
| 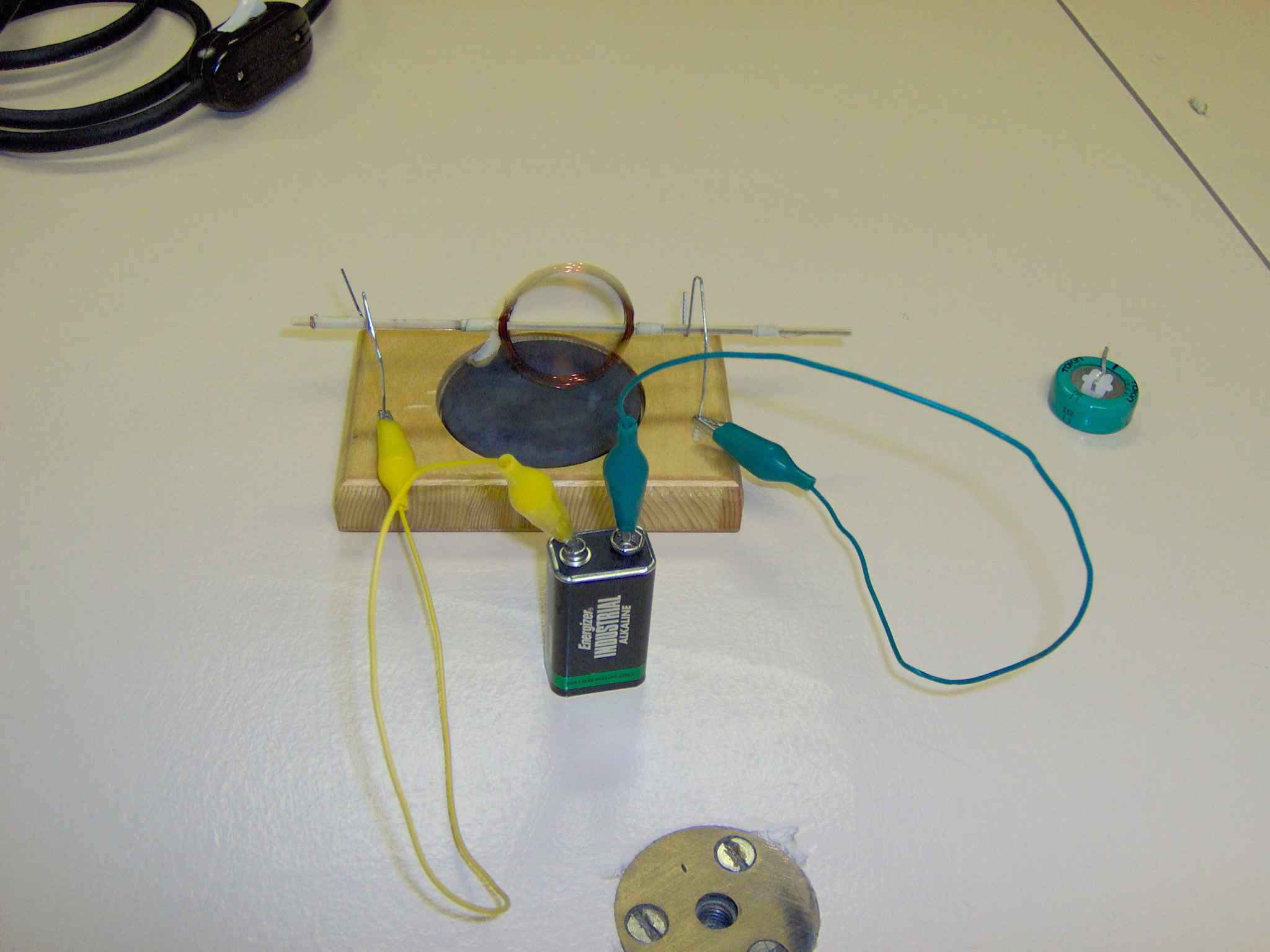
A simple electric motor can be made by attaching a coil of wire to a thin wooden
shaft and taping the ends of the wire to either end of the shaft. The shaft can
be supported on two wires (paper clips) attached to the terminals of a battery.
Insullation is scraped from the wires on the shaft so that current flows through
the coil for an instant each time it completes a revolution. While the current
flows, the coil becomes a magnet and is repelled by the magnet on the base of
the motor.
|
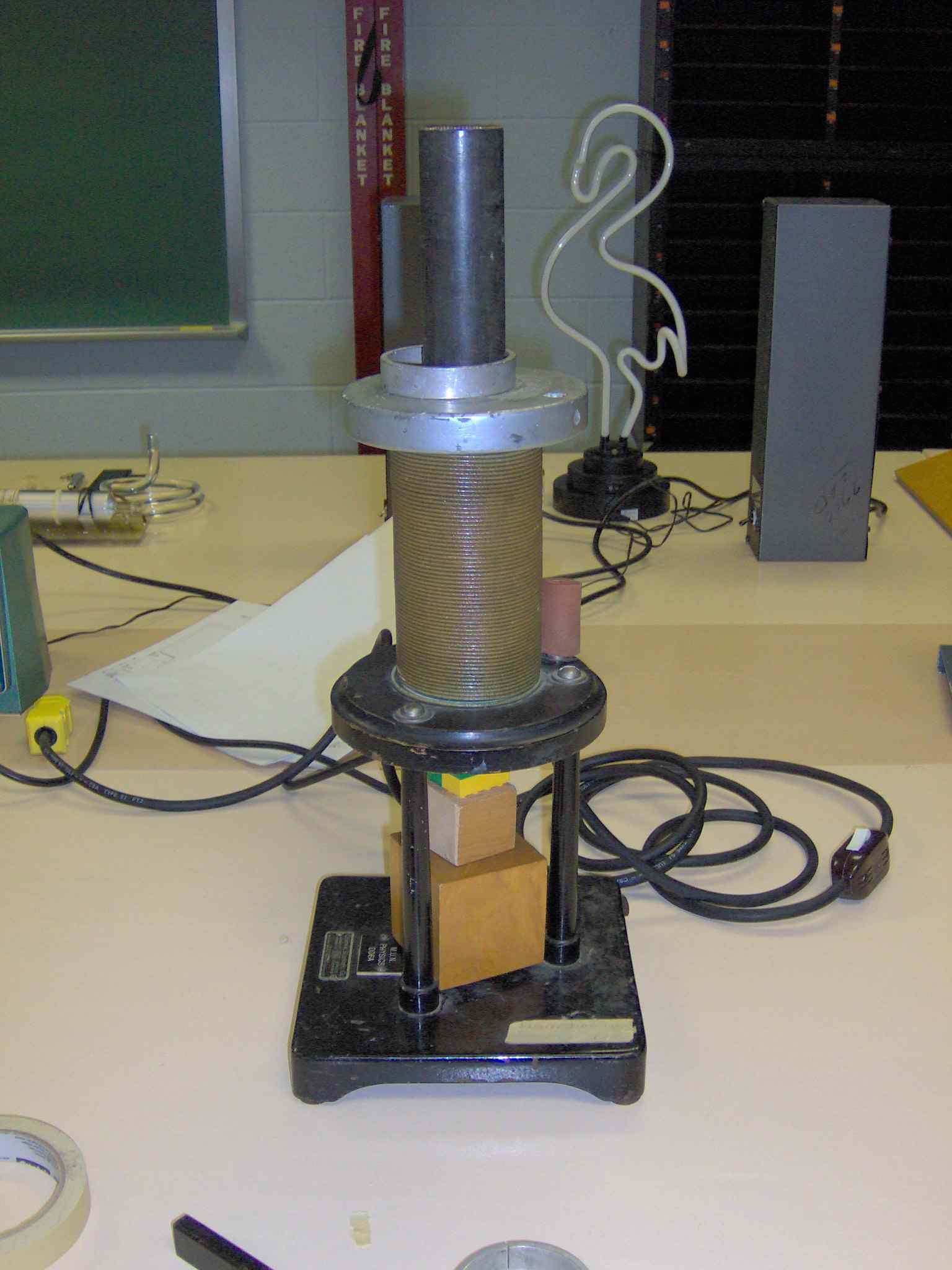

An alternating current through this coil causes an alternating magnetic field
along the axis of the coil. This induces a current around the aluminum ring
above the coil. The magnetic field resulting from the current in the aluminum
ring repels the field in the coil and the ring is levitated (vigorously).
|
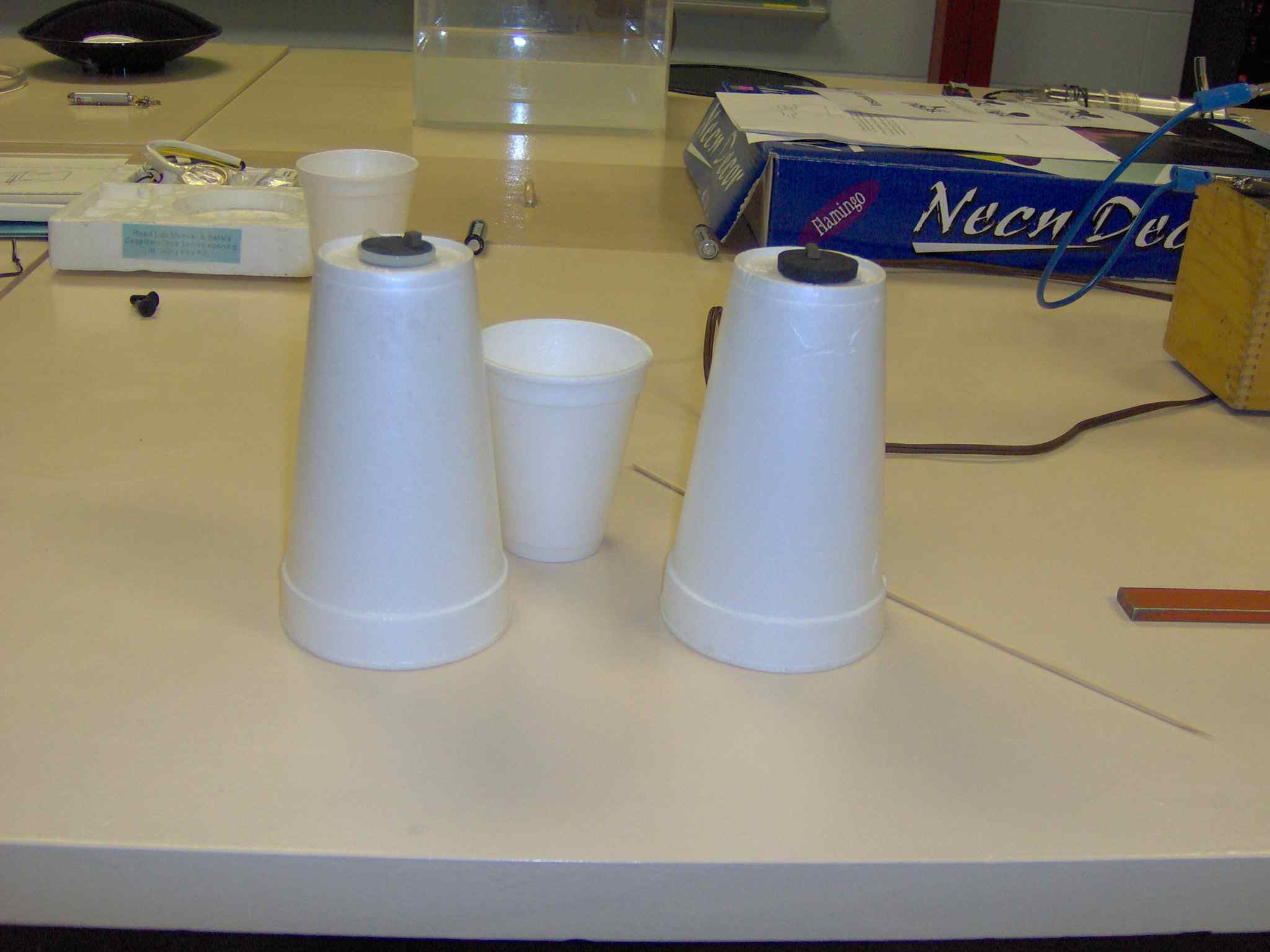

The ceramic, Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide (YBCO), is superconducting at 77 K, the
boiling point of liquid nitrogen. In a superconductor, electrical currents can
flow without resistance and magnetic fields are expelled (the Meissner effect).
A small rare earth magnet placed on a superconducting disc will be levitated as
its magnetic field is expelled from the superconductor.
|
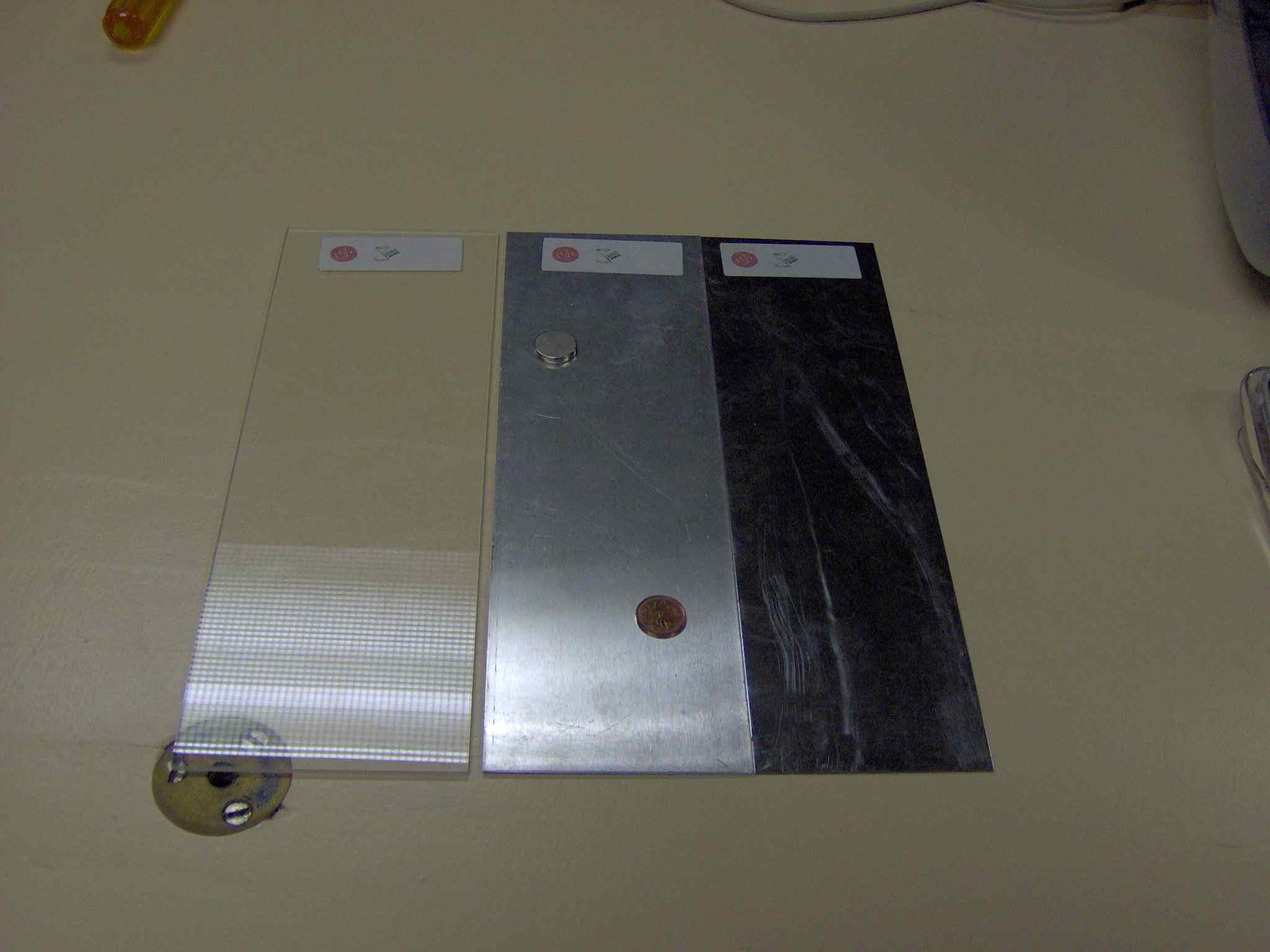

This demonstration of energy lossess due to eddy currents was provided by the
Canadian Association of Physicists to mark the International Year of Physics.
When a penny and a strong magnet are allowed to slide down an inclined
plexiglass sheet, the smooth magnet arrives at the bottom first. The magnet
does not stick to aluminum but when they are allowed to slide down an inclined
aluminum sheet, the magnet is much slower. Most of the gravitational potential
energy of the penny is converted to kinetic energy as it slides but the magnet
induces eddy currents as it slides and some of its gravitational potential
energy is also converted to kinetic energy of the electrons in the aluminum.
|
Light
|